Financial literacy plays a significant role in shaping individuals’ social development by equipping them with essential skills and knowledge to navigate economic challenges, make informed decisions, and contribute meaningfully to society. This blog explores the importance of financial literacy in social development, its impact on personal and community well-being, and strategies for promoting financial education.
Understanding Financial Literacy
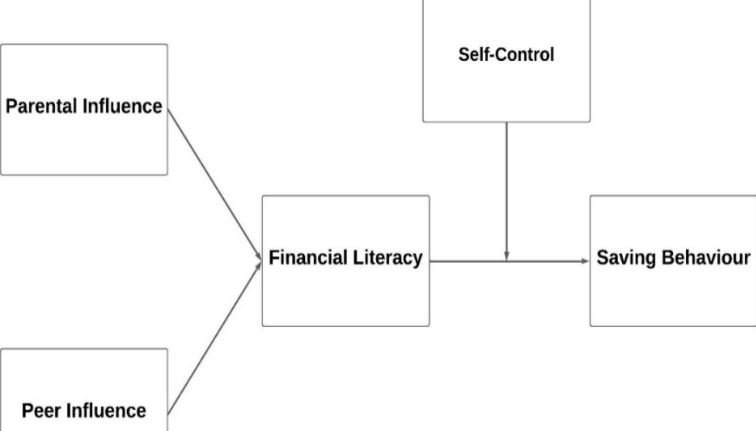
Financial literacy refers to the ability to understand and effectively manage financial resources. It includes skills such as budgeting, saving, investing, understanding credit and debt, and making informed financial decisions based on economic circumstances.
Impact of Financial Literacy on Social Development
Economic Empowerment and Stability
Financially literate individuals are better equipped to manage their finances, build savings, and plan for the future. This economic stability promotes confidence, reduces financial stress, and enhances overall well-being, contributing to a healthier society.
Responsible Citizenship and Civic Engagement
Understanding financial systems and policies empowers individuals to participate in civic life effectively. Financially literate citizens can advocate for financial reforms, support community initiatives, and contribute to economic growth and sustainability.
Reducing Socioeconomic Disparities
Financial literacy helps individuals from diverse backgrounds access opportunities for economic advancement. By promoting financial inclusion and equality, it mitigates socioeconomic disparities and fosters social mobility.
Strategies for Promoting Financial Literacy
Early Education and Curriculum Integration
Integrate financial literacy into educational curricula from an early age to build foundational knowledge and skills. Incorporate age-appropriate lessons on saving, budgeting, and understanding money management principles.
Practical Learning Opportunities
Provide practical learning experiences such as simulations, budgeting exercises, and real-world financial decision-making scenarios. Hands-on activities enable individuals to apply financial concepts and develop critical thinking skills.
Community Outreach and Partnerships
Collaborate with community organizations, financial institutions, and local businesses to offer workshops, seminars, and resources on finance education. Engage diverse audiences and tailor programs to address specific needs and challenges.
Promoting Financial Wellness and Resilience
Financial Planning and Goal Setting
Encourage individuals to set financial goals, create budgets, and develop saving habits. Goal-oriented planning instills discipline, motivates behavior change, and supports long-term financial stability.
Understanding Credit and Debt Management
Educate individuals on responsible borrowing practices, credit scores, and debt management strategies. Empower them to make informed decisions about loans, credit cards, and financial obligations to avoid financial pitfalls.
Investing in Financial Education Initiatives
Allocate resources and support initiatives that promote financial education in schools, workplaces, and community settings. Invest in training educators, developing educational materials, and conducting outreach campaigns to raise awareness.
Conclusion
Financial literacy is a critical component of social development, empowering individuals to achieve economic independence, participate actively in society, and contribute to community well-being. By fostering financial knowledge, skills, and responsible financial behaviors, we can build a more equitable and prosperous society for future generations.